Body image refers to how individuals perceive, think and feel about their bodies. It encompasses beliefs about one’s appearance, including size, shape, and weight. In today’s society, where ideals of beauty are often narrowly defined and perpetuated through media and cultural influences, many individuals struggle with body dissatisfaction. Samvedna Care believes several factors, such as cultural standards, media representation, personal experiences, and social interactions, can influence this perception. A positive body image involves accepting and appreciating one’s body, while a negative one can lead to dissatisfaction. This dissatisfaction can sometimes escalate into serious mental health issues, such as eating disorders. Understanding the complex interplay between body image and eating disorders is crucial for effective prevention and intervention strategies.
Body Image and Eating Disorders:
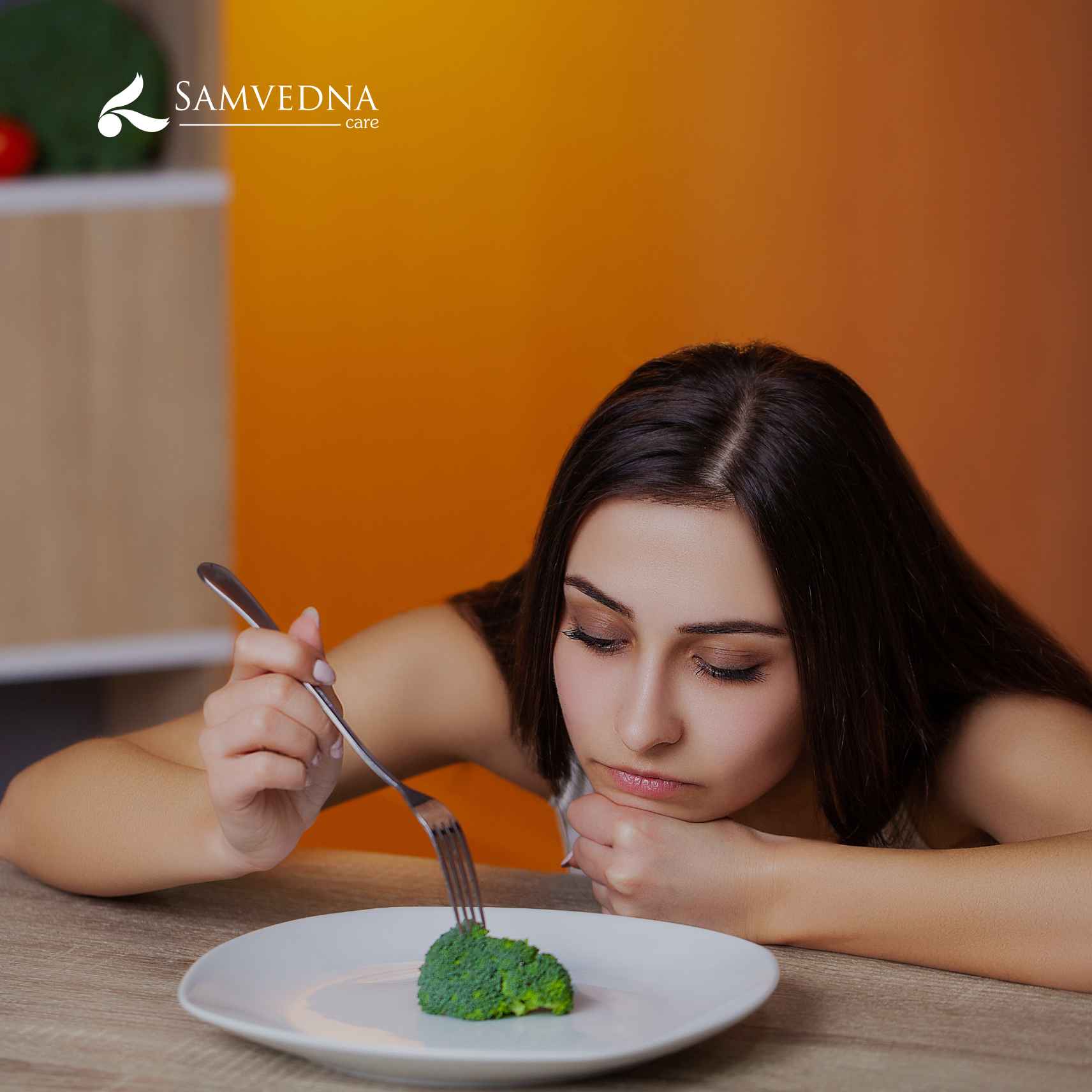
Eating disorders are serious mental health conditions characterized by abnormal eating habits that negatively affect a person’s physical and emotional well-being. Common eating disorders include:
1. Anorexia Nervosa: Characterized by extreme food restriction, an intense fear of gaining weight, and a distorted body image.
2. Bulimia Nervosa: Involves cycles of binge eating followed by compensatory behaviors like vomiting, excessive exercise, or laxative use.
3. Binge-Eating Disorder: Marked by recurrent episodes of eating large quantities of food, often rapidly and to the point of discomfort, accompanied by feelings of loss of control and shame.
These are the mental health conditions characterized by abnormal eating habits and severe distress about body weight or shape. Negative body image is a significant risk factor for the development of eating disorders. When individuals perceive their bodies negatively, they may engage in unhealthy behaviors in an attempt to control their weight and shape. Here are some ways in which body image influences eating disorders:
1. Trauma and stress: Individuals with a negative body image often see themselves as overweight or unattractive due to certain traumas in their lives, regardless of their actual size. This distorted self-perception can drive them to adopt extreme measures to alter their appearance, leading to eating disorders.
2. Psychological factors: Many people with eating disorders have obsessive tendencies and feel a need to exert control over their bodies. They may believe that achieving a certain body type will lead to happiness, acceptance, and self-worth, fueling disordered eating patterns.
3. Social and cultural factors: Cultural and societal standards that idealize thinness and stigmatize larger bodies can exacerbate body dissatisfaction. Media portrayals of unrealistic body types create a false benchmark for beauty, pressuring individuals to conform and potentially triggering eating disorders.
4. Perpetuating factors: For some, disordered eating serves as a coping mechanism to manage negative emotions or stress. The pursuit of an ideal body can become a way to gain a sense of control and self-esteem, albeit temporarily.
Prevention and Intervention
Addressing the relationship between body image and eating disorders requires a multifaceted approach:
1. Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about the dangers of negative body image and promoting body positivity can help individuals develop a healthier perception of themselves. Educational programs can debunk myths about body size and encourage acceptance of diverse body types.
2. Media Literacy: Teaching media literacy can help individuals critically evaluate the images and messages they consume. Understanding the role of photo editing, filters, and selective portrayal can reduce the impact of unrealistic standards.
3. Therapeutic Interventions: Therapeutic approaches, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), are effective in addressing body image issues and eating disorders. Mental health therapists, through online counselling can help individuals challenge distorted thoughts about their bodies and develop healthier coping mechanisms. Therapy can also address underlying emotional issues contributing to disordered eating.
4. Support Systems: Creating supportive environments through open conversations about body image and eating disorders within families, schools, and communities is vital. Building strong support systems provides individuals with the emotional backing they need to seek help and recover. Encouraging dialogue and understanding can significantly impact a person’s journey toward a healthier body image.
5. Self-Compassion and Mindfulness: Practices like mindfulness and self-compassion can foster a more positive relationship with one’s body. Learning to appreciate the body for its functions rather than its appearance can shift the focus from aesthetics to overall well-being.
The relationship between body image and eating disorders is complex, but through increased awareness, education, and support, individuals can develop a healthier body image and prevent the onset of eating disorders. By promoting self-acceptance and challenging societal norms, we can create a culture where everyone feels valued and respected, regardless of their body size or shape. Samvedna Care offers a wide range of therapists, tools, and communities to assist you in various aspects of life. Visit Samvedna Care today and experience a sense of connection and belonging to manage these emotions.
#Ways #Body #Image #Influences #Eating #Disorders








.JPG)